Ribbon and Toolbars
Introduction:
An Excel workbook contains a Ribbon located at the top of the worksheet which houses related commands together in groups. These commands typically represent the most used elements of a group of commands. Excel also contains multiple toolbars that help in the customizing of a worksheet and workbook.
Learning:
THE EXCEL RIBBON
Excel’s features and commands are found in the Ribbon, which is the upper area of the Excel screen that contains several tabs running across the top. Each tab provides access to a different set of Excel commands. The tabs, both standard and contextual, contain groups of related commands specific to the tab.
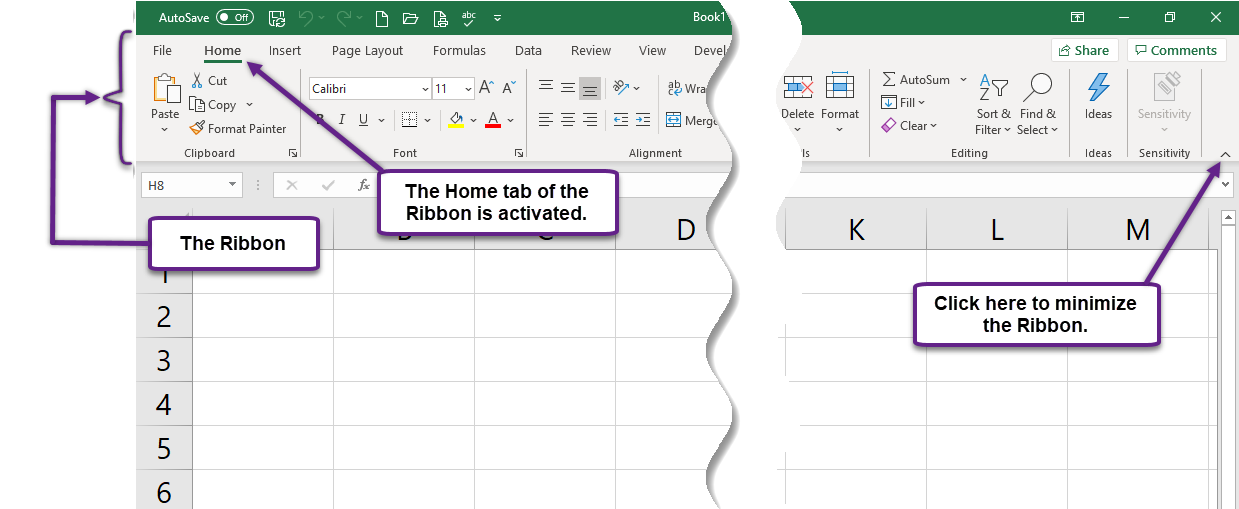
Tabs
The Ribbon is divided into Tabs which represent the major tasks that can be applied to or utilized in Excel. The tabs are displayed across the top of the Ribbon and consist of the File, Home, Insert, Draw, Page Layout, Formulas, Data, Review, View, and Help tabs. Each tab contains multiple groups of subtasks and displays the most common commands on the Ribbon. When the user selects a specific tab, the options on the ribbon change to the available menu items for that given tab.
Command Overview for Each Tab of the Ribbon
|
Tab Name |
Description of Commands |
|
File |
Also known as the Backstage view of the Excel workbook. Contains all commands for opening, closing, saving, and creating new Excel workbooks. Includes print commands, document properties, e-mailing options, and help features. The default settings and options are also found in this tab. |
|
Home |
Contains the most frequently used Excel commands. Formatting commands are found in this tab along with commands for cutting, copying, pasting, and for inserting and deleting rows and columns. |
|
Insert |
Used to insert objects such as charts, pictures, shapes, PivotTables, Internet links, symbols, or text boxes. |
|
Page Layout |
Contains commands used to prepare a worksheet for printing. Also includes commands used to show and print the gridlines on a worksheet. |
|
Formulas |
Includes commands for adding mathematical functions to a worksheet. Also contains tools for auditing mathematical formulas. |
|
Data |
Used when working with external data sources such as Microsoft® Access®, text files, or the Internet. Also contains sorting commands and access to scenario tools. |
|
Review |
Includes Spelling and Track Changes features. Also contains protection features to password protect worksheets or workbooks. |
|
View |
Used to adjust the visual appearance of a workbook. Common commands include the Zoom and Page Layout view. |
Contextual Tabs
In addition to the standard tabs found on the Ribbon, when you have elements within a worksheet selected like a chart, image, or shape that automatically appear and allow you specific editing for these elements. The contextual tabs will display to the right of the Help tab on the Ribbon.
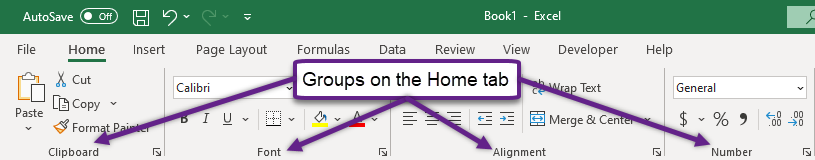
Groups
Groups are found on each tab and relate to the main commands grouped by sub tasks. For instance, the Home tab includes the Clipboard, Font, Alignment, Styles, Cells, Editing, and Ideas groups. Some groups have additional subtasks which can be found by clicking the Dialog Box Launcher (a small box with arrow button in the lower right-hand corner of a group) which opens a separate window with more subtasks to choose from.
Excel Toolbars
Toolbars in Excel provide specific details and the ability to perform actions more easily.
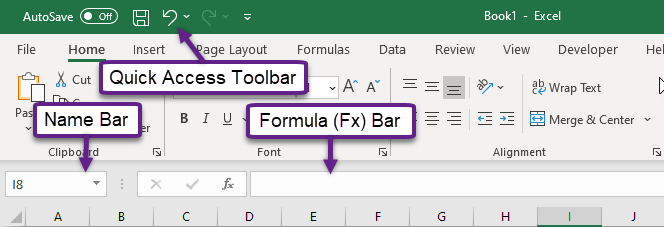
Name Bar
The Name bar provides the address of the selected active cell and resides on the same bar as the Formula bar.
Formula (Fx) Bar
The Formula bar displays the contents within a selected cell and is located to the right of the Name bar. This is where functions, formulas, and data appear when a cell is selected.
Quick Access Toolbar
The Quick Access toolbar provides a customizable option to add additional commands to a toolbar, such as Print, Save As, Save, Close, etc. These common tasks can be added or deleted from the Quick Access toolbar by using the dropdown menu located to the right of the toolbar.
Title Bar
The Title bar located above the Ribbon, shows the file name and also provides information, like when sheets are grouped to let the user know there is a special action being performed.
Help (Search) Box
In addition to the Help tab Excel also provides a Help/Search box which is located above the Ribbon, that allows users to search for assistance by detailing what they need help with. The Help feature provides extensive information about the Excel application. Although some of this information may be stored on your computer, the Help window will automatically connect to the Internet, if you have a live connection, to provide you with resources that can answer most of your questions. You can open the Excel Help window by clicking the question mark in the upper right area of the screen or ribbon. With newer versions of Excel, use the query box to enter your question and select from helpful option links or select the question mark from the dropdown list to launch Excel Help windows.
Toolbars at the bottom on the Worksheet

Status Bar
The Status Bar is located below the worksheet tabs on the Excel screen. It displays a variety of information, such as the status of certain keys on your keyboard (e.g., CAPS LOCK), the available views for a workbook, the magnification of the screen, and mathematical functions that can be performed when data are highlighted on a worksheet.
Zoom Control Bar
The Zoom Control bar is part of the Status bar and allows users to zoom in and out of worksheets. To use the Zoom Control, move the slide bar, or you can choose a number in for a custom zoom by clicking on the 100% number to the right of the bar (this may be larger or smaller if the zoom has been changed).
Summary:
The Ribbon and Toolbars allows Excel users to easily find the most common commands and tasks easily. The grouping of like commands into major and subtasks provides an easy way to find commands and apply them to a worksheet. The Toolbars provide detailed information and the ability to find and adjust worksheet elements. Also, Excel provides users with two ways to get help using the Help tab or the Help/Search box.
Sources:
Beginning Excel by Noreen Brown, Barbara Lave, Julie Romey, Mary Schatz, Diane Shingledecker is licensed under CC BY 4.0
IDM