Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
All living organisms are composed of cells and have the following similarities:
- All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane comprised of phospholipids and proteins
- All cells use DNA as their genetic material
- All cells contain ribosomes, which are specialized at producing the proteins found in the cells
For all the different, diverse living organisms, there are only two basic types of cells found on earth:
- Prokaryotes
- Eukaryotes
Let’s explore each in more detail now…
Prokaryotes
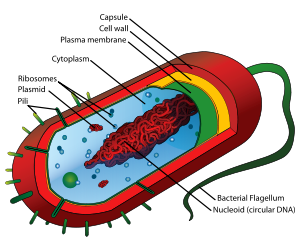
Below are some of the key characteristics which distinguish the prokaryotes:
- Simplest, yet most abundant (in terms of total number of organisms) life forms on earth
- Represent all types of bacteria.
- Typically smaller than eukaryotes (less than 5 micrometers in size; 1 micrometer = 1 millionth of a meter)
- Do Not contain a membrane-enclosed nucleus or any other organelles (see below)
- Named from the Greek terms ‘pro’ (before) and ‘karyon’ (nut/kernel)
- Prokaryotes store their genetic information (DNA) within the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes

Below are some of the key characteristics which distinguish the eukaryotes:
- Larger, more complex cells
- Found in all animals, plants, fungi and protists
- Named due to the presence of membrane-enclosed nucleus which houses the cell’s genetic information (DNA)
- Nucleus = from Greek terms ‘eu’ (true/well) and ‘karyon’ (nut/kernel)
- Eukaryotes are structurally and functionally diverse due to the presence of specialized sub-structures found within the cytoplasm called ‘organelles’.
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
The video below discusses the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
Summary
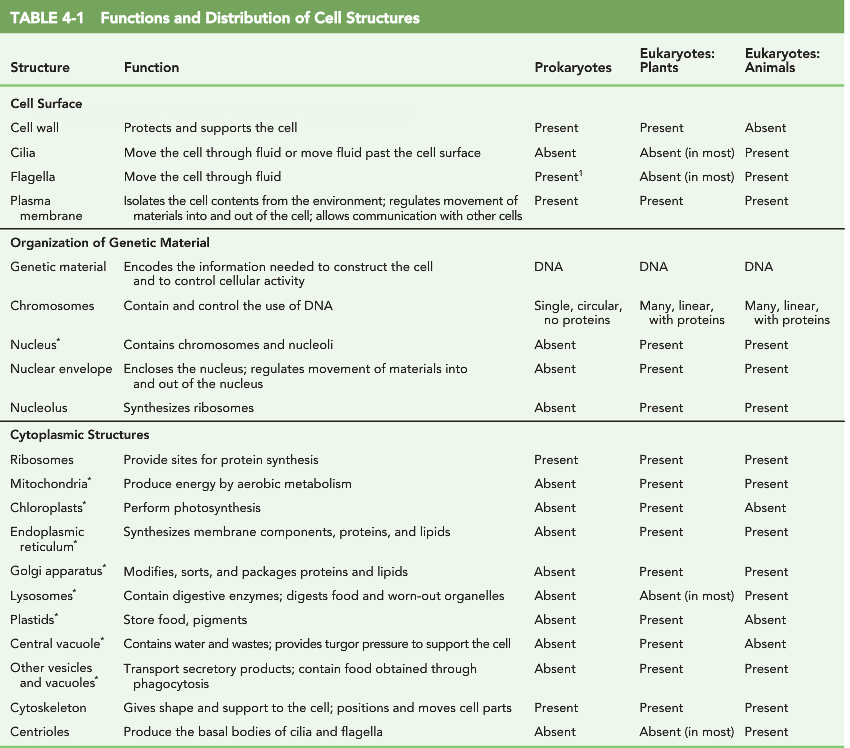
Table 4-1 in your text summarizes some of the more significant, key differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes (with additional distinction between plant and animal eukaryotic cells).