Types of Protein – Nutritional Value
Different Types of Proteins
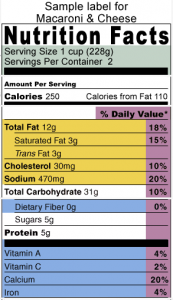
In the sample Nutritional Label, 1 serving(s) of Macaroni and Cheese would contain:
- 250 Calories
- 5 grams of Protein
Summary
Proteins are large, complex molecules made up of amino acids that are critical components of all body tissues. Of the 20 amino acids in the body, nine are essential to obtain from food because our bodies do not synthesize these nine. Protein digestion into individual amino acids occurs mainly in the stomach and small intestine. Once absorbed, amino acids can then be assembled into the proteins required by the body. Functions of proteins are varied and include cell growth, repair, and maintenance. Proteins act as enzymes and hormones and help maintain fluid/electrolyte balance, acid–base balance, and a strong immune system. They transport and store nutrients and supply energy when fat and carbohydrate are limited.
Protein quality is mostly determined by the completeness of amino acid content; therefore, animal products, soy, and legumes contain the highest-quality protein. High protein intake may lead to high blood cholesterol and put added stress on the kidneys in individuals who are susceptible to kidney disease. Good sources of protein include meats, dairy products, eggs, legumes, whole grains, and nuts. Inadequate protein intake can result in protein-energy malnutrition that in extreme cases may take the form of kwashiorkor or marasmus.