Lysosomes
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are specialized structures in the cell which contain enzymes used to digest macromolecules; they act like the cell’s recycling center.
Lysosomes
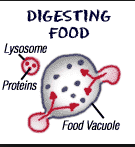
Lysosomes are specialized structures in the cell which contain enzymes used to digest macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. They are characterized by having a relatively acidic interior which is required for the various lysosomal enzymes to carry out the function (similar to the acidity of your stomach). These tiny organelles are designed to ‘fuse’ with other membrane-bound compartments storing food or other material, resulting in the release of digestive enzymes into the compartment where they begin the process of breaking down the larger molecules.
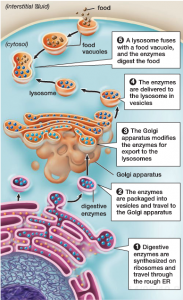
The breakdown of macromolecules in the lysosome results in products including simple sugars, amino acids, and lipids. These products are then transported across the lysosomal membrane into the cytoplasm where they can be utilized by the cell.
In the manufacturing plant example, the lysosome would be similar to a department responsible for recycling materials to be used for additional manufacturing.

The video below discusses the function of lysosomes inside the cell:
Summary
Lysosomes are small structures in the cell which contain digestive enzymes used to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. They are like tiny ‘stomachs’ inside the cell, acid and all!
