Cell Theory
Cell Theory of Life
Most cells are tiny; so tiny, in fact, that it wasn’t until the invention of the microscope in the 1600s that humans were aware of the existence of this minuscule building blocks of life. Once the existence of cells was recognized, it took scientists many more years to truly understand the significance of these important units.
In the 1800s, several scientists investigating cells were able to devise what is known today as the ‘Cell Theory of Life’, which describes common attributes of cells. Contributors to this theory included Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.


The Cell Theory has become accepted as one of the most fundamental concepts in biology. The Cell Theory consists of three key principles:
- Every organism is comprised of one or more cells
- The cell is the most basic unit of life
- All cells are derived from preexisting cells
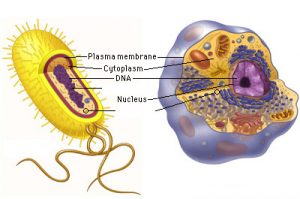
Through further scientific investigation of cells over the ensuing centuries, scientists have also discovered that all cells share other properties, including:
- A plasma membrane which surrounds the cell and separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment. The plasma membrane also plays a significant role in regulating the transport of water and nutrients across its boundary
- The presence of cytoplasm, a fluid environment inside of the cell, containing water, salts and various macromolecules. Most of the chemical reactions that support life occur in the cytoplasm.
- The use of DNA as genetic material. DNA provides the genetic blueprint necessary to allow cells to reproduce and carry out their specific function(s) while the RNA molecule represents copies of specific genes which are used to build proteins inside the cell.
Cell Theory of Life
The video below presents the key principles of the ‘Cell Theory of Life’
Summary
The Cell Theory has become accepted as one of the most fundamental concepts in biology. The Cell Theory consists of three key principles:
-
- Every organism is comprised of one or more cells
- The cell is the most basic unit of life
- All cells are derived from preexisting cells