Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are very important biological molecules which provide the basis for genetic inheritance and for powering the billions of chemical reactions that occur in the body on a daily basis. In this activity, we will explore the structure and function of nucleotides in biological systems.
Nucleic Acids
You are likely familiar with the molecule DNA; DNA stands for ‘DeoxyriboNucleic Acid’ and it is the key molecule used to store and transmit genetic information in organisms. DNA, like all nucleic acids, is assembled from smaller subunits called Nucleotides. Let’s explore the nature of Nucleotides now…
Nucleotides
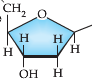
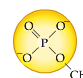
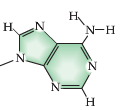
Nucleotides all share a common chemical structure consisting of:
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
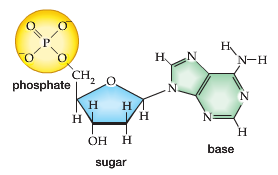
When combined, the final nucleotide structure appears as follows:
Summary
In this lesson, you have learned that:
- Nucleotides are the subunits or building blocks of lager Nucleic Acid molecules
- Nucleotides consist of a central 5-Carbon sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a Phosphate Functional Group, and a Nitrogen/Carbon containing base.
- For DNA, the 4 bases are:
- Adenine
- Thymine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- For RNA, the 4 bases are:
- Adenine
- Uracil
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Nucleotides serve the following functions:
- Carry and store genetic information
- Energy Transport
- Messaging