Mitochondria
Introduction
Mitochondria specialize at producing energy-rich ATP for use throughout the cell cytoplasm. Let’s explore the structure and function of these important organelles now.
Learning
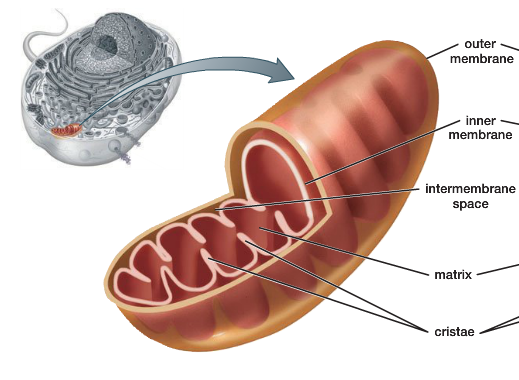
Mitochondria are pod-shaped structures surrounded by a double membrane. The inner mitochondrial membrane has distinct folds, called cristae, while the space between the two membranes is referred to as the intermembrane space. The space found within the inner membrane is called the matrix.
Mitochondria specialize at producing energy-rich ATP for use throughout the cell. Production of ATP is facilitated through a series of chemical reactions which break down glucose in the presence of oxygen. Mitochondria are often referred to as the ‘powerhouse’ of the cell.
In the manufacturing analogy, the mitochondria would represent the power plant, driving and powering the activities of the entire plant.
Mitochondria have a double membrane surrounding it. The Endosymbiotic Theory states that mitochondria evolved from an aerobic bacterium that was engulfed and was “living” within the eukaryotic cell. This would account for the double membrane and the fact that each mitochondrion have their own piece of DNA.
Summary
Mitochondria are pod-shaped structures specialized at producing energy-rich ATP for use throughout the cell cytoplasm.
The Endosymbiotic Theory postulates that the double membrane surrounding, and the DNA present came from an aerobic bacterium that was engulfed and was living inside the eukaryotic cell.
Sources:
Endosymbiosis. (2021, February 10). Retrieved May 20, 2021, from https://bio.libretexts.org/@go/page/49485
