Endomembrane System
Introduction
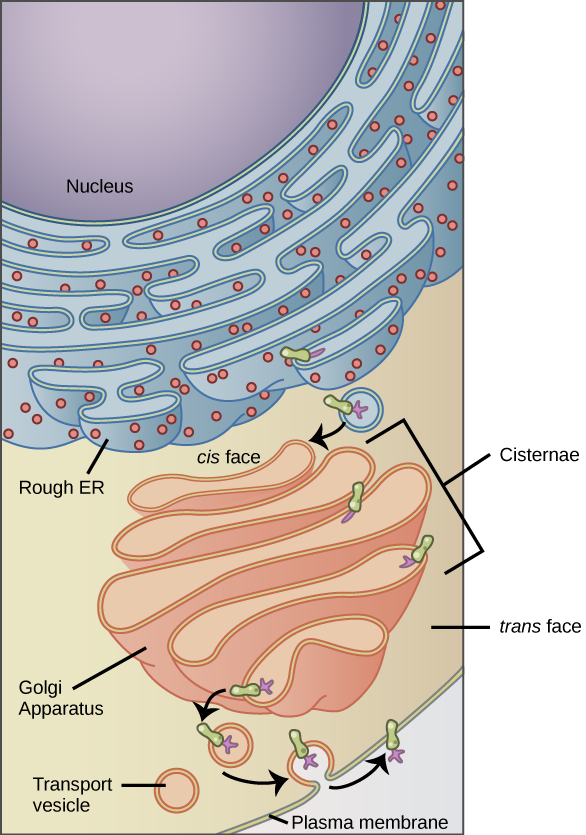
The endomembrane system (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the endomembrane system because, as you will see, it interacts with the other endomembranous organelles. The endomembrane system does not include either mitochondria or chloroplast membranes.
Learning
Endoplasmic Reticulum
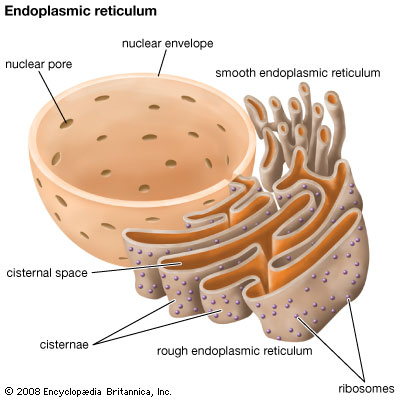
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an extensive and complex network of interconnected tubes and flattened sacs making up over 50% of the total amount of membrane found in the cell. The ER is surrounded by a single membrane that is connected to the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. The ER plays a major role in producing all of the phospholipids used for membrane construction in the cell as well as protein production; proteins destined for other cellular compartments, for the plasma membrane, or for export from the cell are produced in the ER.
In the manufacturing plant example where the nucleus functions as the administrative offices of the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum can be viewed as the factory floor where the cell’s chemical building blocks are assembled. The endoplasmic reticulum serves as the assembly line of the cell.
Inside the cell, there are two types of ER which differ in appearance and function:
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER)
Rough ER
- Portions of the ER membranes have small, rounded particles associated with them that are exposed to the cytosol. Such ER is referred to as rough ER, and the particles are ribosomes.
- Ribosomes manufacture proteins using amino acid building blocks by following instructions provided by DNA in the nucleus.
- Ribosomes attached to the rough ER manufacture proteins that are destined for the ER interior, for insertion into a membrane (including the plasma membrane), or for export from the cell.
Smooth ER
- In some cells, a percentage of the ER membrane lacks ribosomes and is therefore called smooth ER. The smooth ER provides sites where portions of the ER membrane actively bud off to produce vesicles, small containers which contain a small portion of the ER interior. These vesicles are then transported to other regions of the cell.
- In some cells, smooth ER is used to produce large quantities of lipids such as steroid hormones. Smooth ER is also abundant in liver cells, where it contains enzymes that detoxify harmful drugs such as alcohol and metabolic wastes such as ammonia.
- In the manufacturing plant example, vesicles are like carts used to transport goods between different departments.
Golgi Apparatus
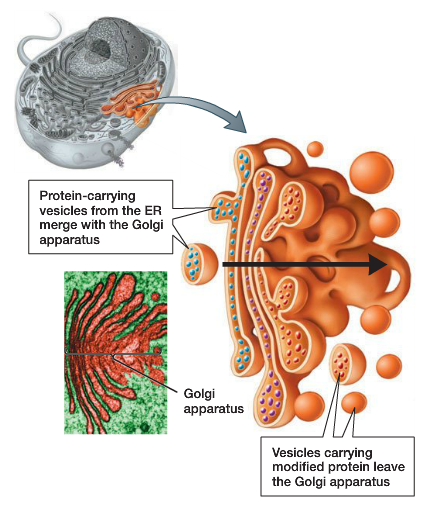
- The receiving side of the Golgi apparatus, which receives vesicles from the ER is called the cis face; the opposite side is the trans face.
- Transport vesicles from the ER fuse with the cis face and empty their contents into the lumen of the Golgi apparatus.
- As the proteins and lipids travel through the Golgi, they are further modified so they can be sorted.
- This often involves adding short chains of sugar molecules.
- The modified and tagged proteins are packaged into secretory vesicles that bud from the Golgi’s trans face.
- Some of these vesicles deposit their contents into the cell, where they will be used, other vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents outside the cell.
- In plant cells, the Golgi has the additional role of synthesizing polysaccharides used in parts of the plant
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are specialized structures in the cell which contain enzymes used to digest macromolecules; they act like the cell’s recycling center.
Lysosomes are specialized structures in the cell which contain enzymes used to digest macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- They are characterized by having a relatively acidic interior which is required for the various lysosomal enzymes to carry out the function (similar to the acidity of your stomach).
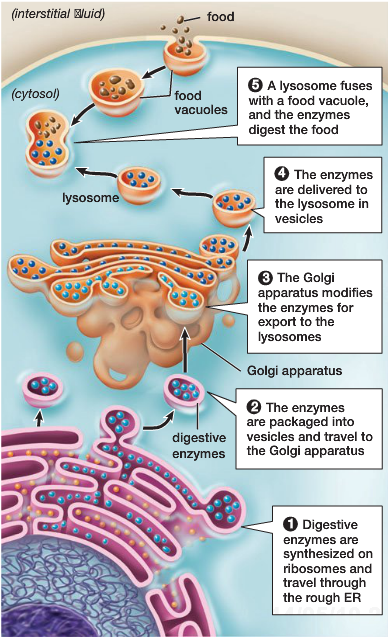
- These tiny organelles are designed to ‘fuse’ with other membrane-bound compartments storing food or other material, resulting in the release of digestive enzymes into the compartment where they begin the process of breaking down the larger molecules.
- The breakdown of macromolecules in the lysosome results in products including simple sugars, amino acids, and lipids. These products are then transported across the lysosomal membrane into the cytoplasm where they can be utilized by the cell.

- In the manufacturing plant example, the lysosome would be similar to a department responsible for recycling materials to be used for additional manufacturing.
Summary
The endomembrane system within eukaryotic cells includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi Apparatus, lysosomes and other vesicles. The Golgi Apparatus appears as a series of flattened membrane-enclosed sacs which serve to process and modify materials (proteins and membranes) which are produced in the ER. Substances which are modified in the Golgi are sorted and packaged into vesicles for transport elsewhere in the cell.
The Golgi Apparatus serves as the shipping department for the cell.
Sources:
“Endomembrane System.” By OpenStax Biology 2e. Retrieved from: https https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/4-4-the-endomembrane-system-and-proteins Licensed under: CC-BY: Attribution