Cytoskeleton (Video)
Introduction
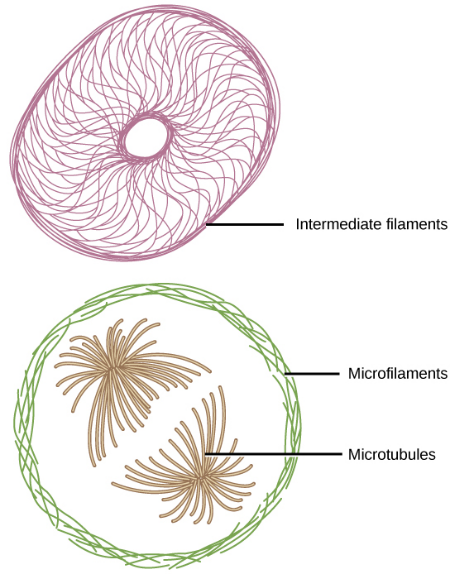
If you were to remove all the organelles from a cell, would the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm be the only components left? No. Within the cytoplasm, there would still be ions and organic molecules, plus a network of protein fibers that help maintain the cell’s shape, secure some organelles in specific positions, allow cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enable cells within multicellular organisms to move. Collectively, scientists call this network of protein fibers the cytoskeleton. There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Here, we will examine each.
Summary
The three types of filaments that make the cytoskeleton are:
- Microfilaments are the narrowest and function in cellular movement
- Intermediate filaments have no role in cell movement, their function is purely structural.
- Microtubules provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell
Sources:
“Cytoskeleton Structure and Function.” YouTube, Uploaded by
National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science, Aug 3, 2015. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/YTv9ItGd050
