Discovery of DNA Structure
Introduction
The mystery of the hereditary material! We knew there was a substance…
- Mendel knew hereditary information was passed on to new generations.
- Determined – 2 factors for every trait.
- 1900’s discovery that proteins & DNA were the molecules that passed on traits, but which one?
- by 1950’s DNA was discovered to be the substance that passed on information.
But we still did not know the structure, and therefore did not know how it worked.
Learning
Determining the shape of DNA was the “once in a lifetime” achievement. There were three well known groups working on this.
- In the US Linus Pauling from Caltech in California was an expert on using x-ray pictures to determine the shape of organic molecules such as the connective tissue in humans. But he was labeled a “subversive” by Sen. McCarthy because of his protests on campus. Therefore, he could not leave the country.
- To collaborate or hear new information in your field during the 50’s you attended conferences – they were held in Europe so he could not attend because he could not leave the country.
- In London there was a group at Kings College that was using the same procedure on DNA – The lead researcher was Wilkins. He hired a woman named Rosalind Franklin who was a pioneer in her day because she was a “woman scientist” educated with a PhD and an expert at performing the x-ray diffraction technique. The male dominated lab researchers thought of her as nothing but an assistant.
- In London at Cambridge – Watson and Crick were good at figuring out data but they didn’t do experiment – just analyzed data that was provided to them.
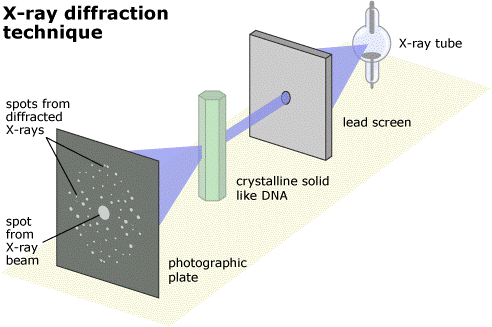
X-Ray Diffraction
The technique used in the 50’s to determine the structure (shape) of a molecule utilized x-rays. All the water was removed from the specimen and it became a crystal. An x-ray beam was focused on the molecule using lead sheets with holes. A photographic plate was placed after the crystal to “catch” or photograph how the x-rays bounced off the molecule. The pattern of the X-rays as they were dispersed through the DNA crystal were captured on the x-ray film. Based on the regularity of the pattern seen on the x-ray film, they were able to make predictions about the size and shape of the DNA molecule.
The x-rays diffracted off the bonds in the molecule – therefore this was called x-ray diffraction.
In 1952 – one of Franklin’s pictures (labeled Photo 51) was dramatically different and she was getting close to determining the structure. At a conference she presented this finding, and everyone was intrigued
Soon after this conference Watson and Crick wrote a letter to the famous Journal ‘Nature’ explaining the structure of DNA. Remember they did not do experiments, just analyzed data. So where did their data come from??
It is believed that someone in Wilkin’s lab provided Watson and Crick with Franklin’s DNA picture! They did not ask Franklin if they could use her data, which was at minimum very unprofessional and disrespectful. They never acknowledged her work especially when they received the Nobel prize.
Watson, Crick, and Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1962 for determining the structure of DNA. Franklin got no recognition – she was dead, died of cancer, and the prize is not awarded posthumously.
The Structure
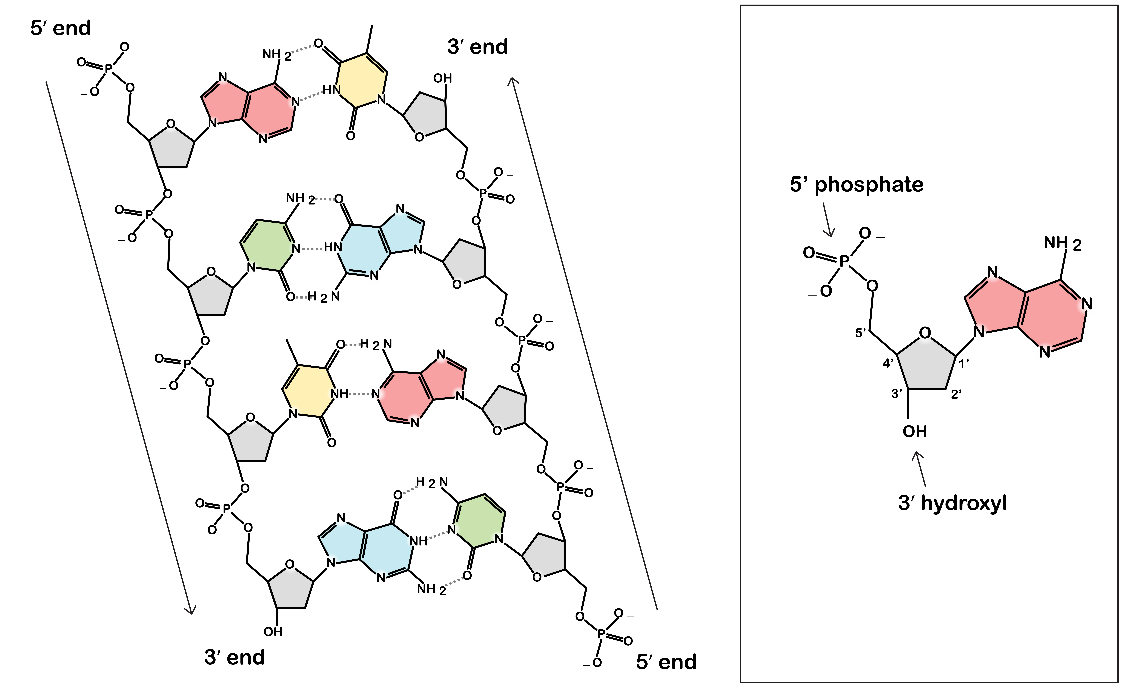
- DNA consists of two nucleotide strands.
- Strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between bases.
- Adenine binds with Thymine & and Cytosine binds with Guanine.
- Molecule is a double helix.
- With ‘turns’ occurring every 3.4 nanometers (1 nanometer = 1/1,000,000,000th of a meter).
- There appeared to be approximately 10 ‘units’ in each turn of the helix.
- The width of the DNA molecule appeared to be about 2 nanometers.
Summary
- Method used – X-Ray Diffraction.
- Multiple groups working on it.
- Franklin’s Photo 51 was the key!
- It was utilized as the foundation for the structure.
Sources:
Photo 51 image modified from “DNA structure and sequencing: Figure 2,” by OpenStax College, Biology (CC BY 3.0)
DNA Image modified from “DNA chemical structure,” by Madeleine Price Ball (CC0/public domain
“DNA structure and sequencing.” by OpenStax College, Biology, CC BY 4.0.
“Historical basis of modern understanding,” by OpenStax College, Biology, CC BY 4.0(Opens in a new window).
Understanding Science. 2021. University of California Museum of Paleontology. 22 May 2021 <http://www.understandingscience.org>.