What is Evolution?
Introduction
Evolution is a term used to describe the overall changes which occur within a population over time. (Population – all individuals of a single species within a particular area).
As explorers and naturalists began to explore far and distant places in the 18th century, they began to recognize and appreciate the incredible diversity of life forms that exist on our planet. At the same time, they also began to recognize distinct patterns and similarities in the appearance of some species within a defined geographic region. Further advances in the science of geology (study of solid earth, rocks, and processes by which they change over time) and evidence found in fossils (preserved remains of organisms long since deceased) around the same time combined with the observations of naturalists and led to the formation of the theory of evolution.
- One important fact that must be understood when studying evolution is that it is based in science and observable facts. Understanding biology, geology, and the scientific method (making observations, testing hypothesis, etc) is crucial to explaining evolution because it is a scientific theory.
- The study of evolution is sometimes considered controversial but why?
- People used to rely on faith to explain our world because at that time they lacked evidence for any other explanation
- We now have evidence to explain many things about our world that were once inexplicable and taken altogether this evidence forms the theory of Evolution
- The transition from believing based on faith alone to accepting evidence and science is challenging for some
Learning
What is Evolution?
The ‘Theory of Evolution’ addresses the question about how life forms have diversified over billions of years on earth. It also explains how modern life forms have adapted to the vast array of environments that exist on earth.
Evolution can be defined as ‘change in heritable traits within a population across generations’.
Three factors contribute to the process of Evolution:
- Reproduction
- DNA Replication
- Mate Selection
As we have learned throughout this course, reproduction is an essential aspect of life on earth. Due to the random alignment of chromosomes when gametes are made in the sex organs this can result in the introduction of small variations in traits from generation to generation over time.
In addition, during DNA Replication errors can be introduced. When this occurs, this generates a ‘mutation’. A mutation is defined as ‘any change in the sequence of the DNA molecule’. Sometimes, these changes are substantial enough to result in changes in appearance or overall function of an organ or limb within an individual. If these changes occur to genes that are packaged into gametes, they can then be passed on to future generations through the process of mating.
The selection of mates has a huge influence on the rate of evolutionary change. The combination of traits present in an individual can make that individual more or less attractive as a potential mate. Traits which make the individual more ‘attractive’ to the opposite sex will have a greater chance of being passed on to the next generation. Over time, this leads to shifts in the appearance of populations over thousands or millions of years.
A great example of how mate selection can influence the appearance of a species is found in the modern dog. While all dogs are members of the same species, variations in breeds have been ‘selected’ by breeders over many generations. ‘Desirable’ traits for particular breeds are sought by dog breeders in a mating pair to maximize the potential that the resulting litter will receive these ‘desired’ characteristics. This is precisely how breeds differ so much in appearance from the Bull Dog to the Great Dane.
The Theory of Evolution also explains how all life forms would have been derived from a common ancestor. Reproduction with variation over billions of years lead to the generation of new species over time and those species have continued to evolve from generation to generation to ensure ongoing survival.
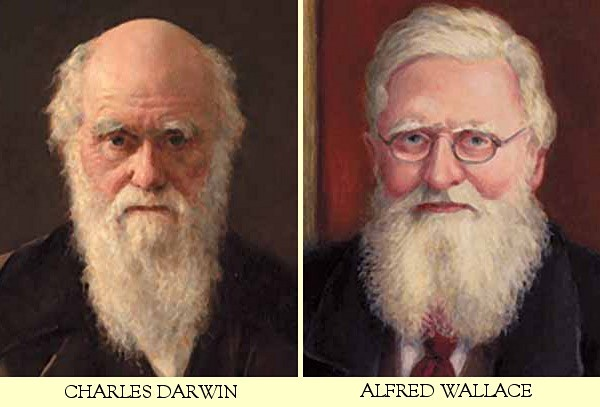
While the processes of generating DNA mutations and the assortment of chromosomes during Meiosis occur completely randomly, the evolution of a species is far from random. As we will learn in this unit, the process of evolution is influenced by several forces, including Natural Selection – a concept introduced by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace. We will discuss Natural Selection more in another lesson.
Summary
Evolution is the process of adaptation through mutation which allows certain characteristics to pass to the next generation. Over time, organisms evolve more characteristics that are beneficial to their survival.
Three factors contribute to the process of Evolution:
- Reproduction
- DNA Replication
- Mate Selection
Sources:
Cynoclub/iStock/ThinkStock, 2021, digital image of Dog Breed Evolution, Smithsonian Science Education Center, May 17, 2021.
“Understanding Evolution.” By OpenStax Biology 2e. Retrieved from https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/18-chapter-summary. Licensed under: CC-BY: Attribution
Evolution and Adaptation. (2020, December 31). Retrieved May 22, 2021, from https://bio.libretexts.org/@go/page/5916